What you need to know about GPS RTK?
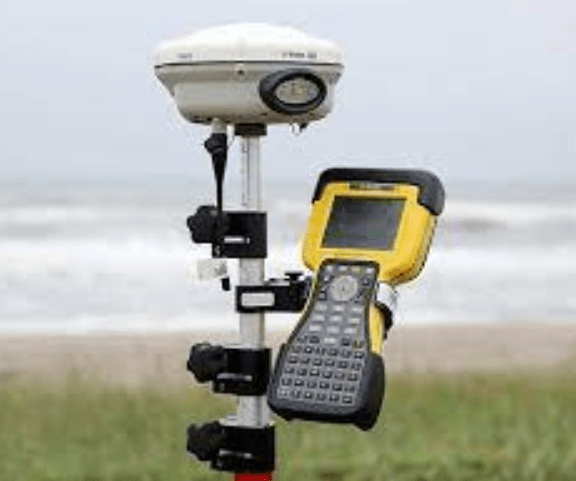

Before deploying GPS RTK, you need to learn its limitations and benefits. Accuracy, limitations, and applications are topics that you need to be aware of. Also, you need to check your base station’s antenna height, and incorrect antenna height is a common mistake. If possible, compare the observations from two or more stations using the same antenna height and make corrections accordingly.
Limit
GPS RTK is an emerging technology that can help users determine objects’ location and their relative position. The technique has many applications. It is helpful for land and hydrographic surveys, measuring the relative position of stationary and moving objects, and testing ADAS systems. However, its limitations are still limiting. Generally, GPS RTK requires observing four or more satellites, and the signal can be volatile if a building or other object blocks one.
To avoid these problems, it is recommended to use GPS RTK when the distance between the base station and rovers is 6-12 miles or less. Depending on the radio data link, the range may be limited. Furthermore, high radio traffic can interfere with the radio signals, reducing the effective range of the baseline. Also, RTK radios operate in frequencies often crowded with emergency voice communications. To avoid this problem, make sure that your base station operates in a channel with little or no radio traffic.
Accuracy
GPS RTK systems are classified into two categories: high-rate and low-rate. High-rate RTK is considered to be the most accurate of all. It is capable of precise positioning and time measurements in a short amount of time. It also supports high-rate positioning. It can be used for base transmission and sensor/rover applications.
Some factors can impair the accuracy of GPS RTK, and these factors include radio interference, ionospheric activity, and multipath. Consequently, GPS RTK data suffers from delays and ambiguities caused by troposphere factors.
One method for improving the accuracy of GPS RTK is real-time kinematics. This technique relies on double-diffusive observables. For example, the phase of a carrier signal is dependent on the speed of light, the carrier wavelength, and other factors, such as atmospheric path and the clocks of the satellite and receiver. The accuracy of GPS RTK is essential in various applications such as mapping projects, autonomous driving, and mapping.
Limitations
One of the key limitations of GPS RTK is it’s time to correct carrier phase observations in real-time. This convergence time varies depending on the processing algorithm used and the distance between the rover and base, and it can be anywhere from a few seconds to minutes. In addition, RTK relies on continuous tracking of GNSS signals to fix the ambiguity. In urban applications, this is not practical. In such instances, RTK is not a viable option.
Another limitation of GPS RTK is its low sampling rate. The sensor can only measure ellipsoidal height differences between two points and cannot detect orthometric height differences between them. Because of this, RTK data may look similar to those obtained through optical surveying with an EDM or a level. Regardless of these limitations, RTK provides many advantages over Bench traditional methods. However, the accuracy of the sensor is not equivalent to a level.
Applications
GPS real-time kinematic positioning (RTK) is a revolutionary surveying technique that improves the precision of position data. The technology combines measurements from a single fixed reference station with an interpolated virtual one to achieve centimeter-level accuracy. Previously, positioning methods required post-processing to ensure accuracy, but RTK eliminates such errors. The technology has many applications, including surveying, hydrographic mapping, unmanned aerial vehicle navigation, and military and aerospace applications.
Other uses for RTK technology include auto drive/autopilot systems, precision farming, and machine control systems. Bench Mark is the USA’s top supplier of RTK GPS systems. You may consult with them and they will help you.
Spirent simulator
The Spirent GPS RTK simulator is a powerful tool for testing and developing location-aware products. It produces a wide range of pseudo-signals from various satellite positioning systems. Its multi-frequency capability and accuracy make it an ideal tool for research, development, and performance testing.
Q Ground Control
Q Ground Control for GPS RTK is an excellent way to determine the current position of your drone, whether you’re flying it for business or pleasure. It comes with several useful features, including an artificial horizon and GPS location. The GPS must be connected to the ground control laptop via wifi or radio telemetry.